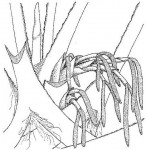
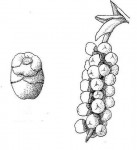
Borassus aethiopum
Selected images: Click on each image to see a larger version and details of the record View all images (19)
Detailed records: Display species records QDS maps by: Google Maps Point records by Google Maps
Species details: Click on each item to see an explanation of that item (Note: opens a new window)
| Synonyms: |
Borassus flabellifer L. var. aethiopum (Mart.) Warb. |
| Common names: | Cibangalala (Bemba) Kahuma (Tonga: Zambia) Kakoma (Nyanja) Kakunka (Lenje) Muhuma (Ila) |
| Frequency: | Locally abundant |
| Status: | Native |
| Description: |
Large palm tree. Stems erect, up to 20 m, with a distinct swelling above the middle. Leaves crowded on top of the stem, fan-shaped, blue-green up to 4 m including the petiole. Petiole armed with recurved thorns. Flowers in large branched sprays, unisexual on separate trees, female flowers larger than male. Fruit large, 12-18 cm in diameter, subspherical, orange-brown. |
| Type location: |
Ghana |
| Notes: |
Major populations were destroyed when the Kafue Gorge dam flooded the habitat. Widespread; not threatened. |
| Derivation of specific name: | aethiopum: Ethiopia, the name of the sub-Saharan biological region before the country formerly known as Abyssinia claimed the name Ethiopia. |
| Habitat: | Floodplain alluvium, munga woodland and wooded grassland on dolomitic soils, and occasionally on termite mounds in miombo woodland. |
| Altitude range: (metres) | 30 - 1200 m |
| Flowering time: | Aug - Oct |
| Worldwide distribution: | Sudanian, Zambezian and Coastal phytochoria, extending to northern South Africa. |
| FZ divisions: | B,N,W,C,E,S |
| Zambian distribution (Provinces): | Nw,Cb,Lp,N,Mc,E,C,Lk,S,(W) |
| Growth form(s): | Tree, shrub over 2 m. |
| Endemic status: | |
| Red data list status: | |
| Insects associated with this species: | Zophopetes dysmephyla (Larval foodplant) |
| Spot characters: | Display spot characters for this species |
| Images last updated: | Monday 27 October 2014 |
| Literature: |
Burrows, J.E., Burrows, S.M., Lötter, M.C. & Schmidt, E. (2018). Trees and Shrubs Mozambique Publishing Print Matters (Pty), Cape Town. Page 51. (Includes a picture). Chapano, C. & Mamuto, M. (2003). Plants of the Chimanimani District National Herbarium and Botanic Garden, Zimbabwe Page 9. Coates Palgrave, K. (revised and updated by Meg Coates Palgrave) (2002). Trees of Southern Africa 3rd edition. Struik, South Africa Da Silva, M.C., Izidine, S. & Amude, A.B. (2004). A preliminary checklist of the vascular plants of Mozambique. Southern African Botanical Diversity Network Report No. 30 Sabonet, Pretoria Page 120. Dransfield, J. (2010). Arecaceae Flora Zambesiaca 13(2) Pages 61 - 63. (Includes a picture). Drummond, R.B. (1975). A list of trees, shrubs and woody climbers indigenous or naturalised in Rhodesia. Kirkia 10(1) Page 232. Fanshawe, D.B. (). District vegetation reports Division of Forest Research, Kitwe (roneo). Fanshawe, D.B. (1971). The Vegetation of Zambia. Division of Forest Research, Kitwe. Fowler, D.G. (2007). Zambian Plants: Their Vernacular Names and Uses, Kew Publishing Golding, J.S. (ed.) (2002). Zimbabwe Plant Red Data List. Southern African Plant Red Data Lists. SABONET 14 Page 162. Mapaura, A. & Timberlake, J. (eds) (2004). A checklist of Zimbabwean vascular plants Southern African Botanical Diversity Network Report No. 33 Sabonet, Pretoria and Harare Meerts, P. & Hasson, M. (2016). Arbres et arbustes du Haut-Katanga Jardin Botanique Meise, Belgique Page 102. (Includes a picture). Ntore, S. & al. (2024). Checklist of the vascular plants of Burundi Page 55. Parker, T. (2023). Common Trees of Mozambique The Tree Press, Austin, Texas, USA Pages 56 - 57. (Includes a picture). Phiri, P.S.M. (2005). A Checklist of Zambian Vascular Plants Southern African Botanical Diversity Network Report No. 32 White, F. (1962). Forest Flora of Northern Rhodesia Oxford Univ. Press. White, F. (1983). The Vegetation of Africa. A descriptive memoir. UNESCO, Paris |
Other sources of information about Borassus aethiopum:
Our websites:
Flora of Burundi: Borassus aethiopumFlora of the DRC: Borassus aethiopum
Flora of Malawi: Borassus aethiopum
Flora of Mozambique: Borassus aethiopum
Flora of Zimbabwe: Borassus aethiopum
Flora of Zimbabwe: cultivated Borassus aethiopum
External websites:
African Plants: A Photo Guide (Senckenberg): Borassus aethiopumAfrican Plant Database: Borassus aethiopum
BHL (Biodiversity Heritage Library): Borassus aethiopum
EOL (Encyclopedia of Life): Borassus aethiopum
GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility): Borassus aethiopum
Google: Web - Images - Scholar
iNaturalist: Borassus aethiopum
IPNI (International Plant Names Index): Borassus aethiopum
JSTOR Plant Science: Borassus aethiopum
Mansfeld World Database of Agricultural and Horticultural Crops: Borassus aethiopum
Plants of the World Online: Borassus aethiopum
Tropicos: Borassus aethiopum
Wikipedia: Borassus aethiopum